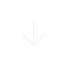Partial vs Total Knee Replacement: Which is the Better Option?
Living with chronic knee pain can limit your physical function, affecting your ability to perform daily activities. While self-management skills, medication, and living a healthy lifestyle help manage chronic pain, it can only offer temporary relief and do not address the problem. In some cases, surgery is the only option to get back to living a pain-free, active life.
Depending on the severity of the knee problem, your healthcare provider may recommend a partial or total knee replacement surgery. You may wonder about what the right option for you is or about the benefits and risks associated with the treatment procedure.
To answer those questions, we need to explore and understand the causes of why you have developed knee joint degeneration. Several causes of complex knee problems include rheumatoid or other types of inflammatory arthritis, infection, or past trauma.
As you age, your knee starts to degenerate. As a result, the cartilage that cushions the knee joints deteriorates. The knee cartilage acts as a shock absorber, minimizing friction and distributing the pressure uniformly between the joints. However, the cartilage does not have the ability to repair itself. This causes the joint bones to rub against each other’s surfaces, resulting in pain and stiffness. This condition is known as osteoarthritis. If medication, cortisone injections, physical therapy, or braces cannot manage the pain, then a knee replacement surgery might be a solution for you.
Anatomy of the Knee
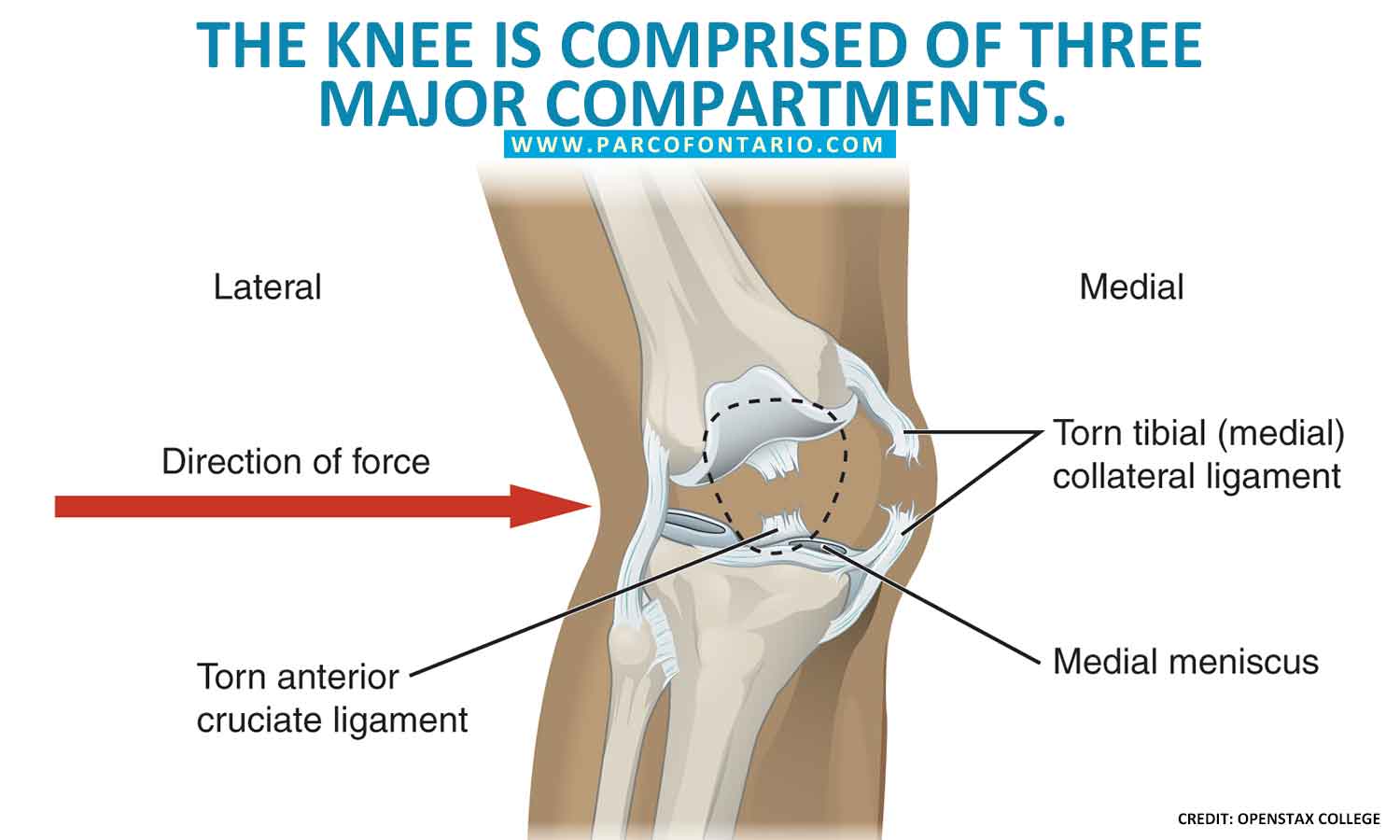
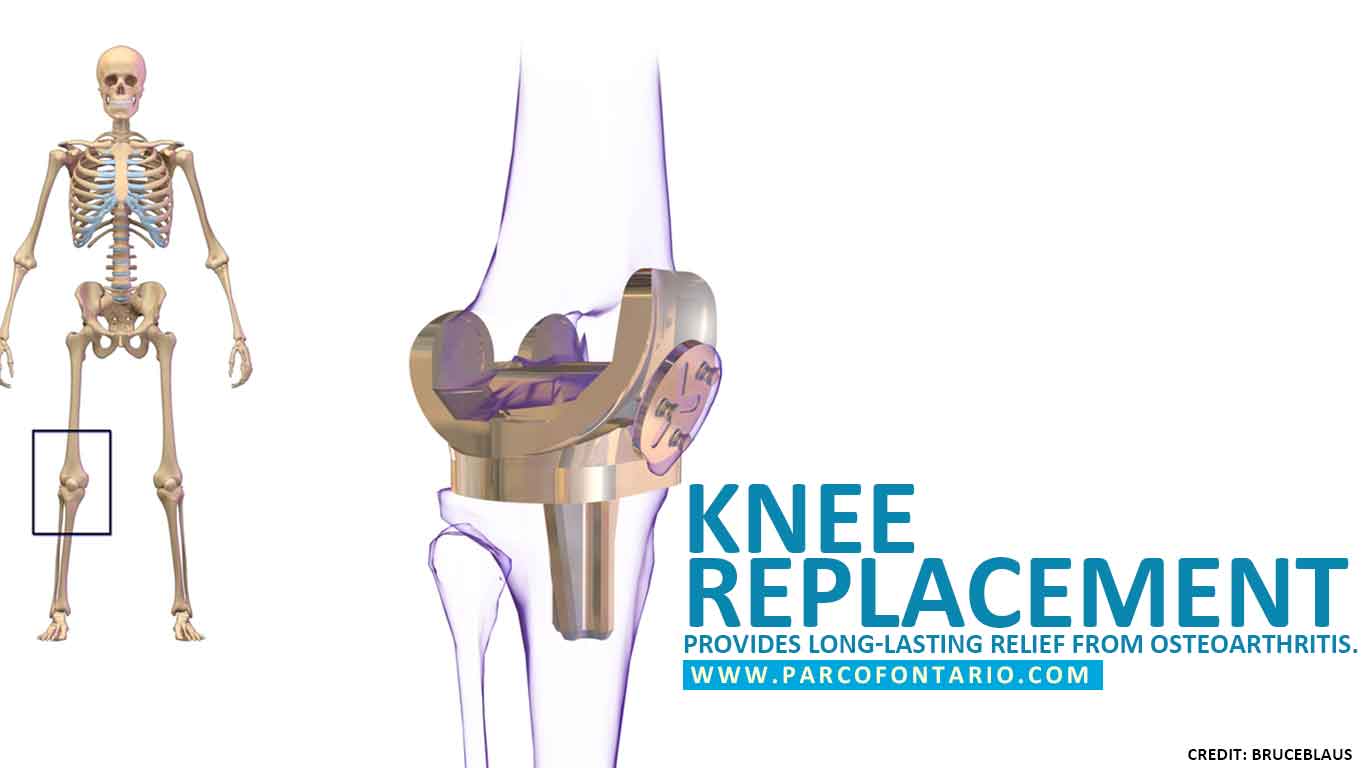
Before you assess what is causing your knee pain and treatment options, you need to understand the parts of your knee. The human knee consists of three compartments: the medial compartment (inner section of the knee), the lateral compartment (outer section of the knee), and the patellofemoral joint (located between the kneecap and thighbone). These three knee compartments have ligaments, tendons, and cartilage that works closely together to enable the knee to function properly.
In some cases, osteoarthritis can only affect one compartment of the knee – usually the medial compartment. Although it can also affect the lateral compartment, it is less likely to happen in osteoarthritic patients.
When to Consider Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee osteoarthritis can be debilitating as it limits your mobility and flexibility. It can make walking, climbing the stairs, and even sitting uncomfortably painful. Signals that your arthritis may need invasive intervention can include:
- Chronic pain that prevents you from performing your everyday activities.
- Severe pain that can be felt even when at rest.
- Persistent inflammation and swelling that does not improve with medications, therapy, or rest.
- Bowing in or out of the leg
However, several things can help manage pain. Healthcare professionals almost always recommend trying less invasive treatment options before resorting to surgery.
- Oral Pain Medications – Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, are over-the-counter pain pills that fight inflammation.
- Injectable Medications – Corticosteroid shots help reduce inflammation and provides fast relief from pain that can last up to a few months. Hyaluronic acid injections can help boost the natural fluid of the joint to help move the knees properly and smoothly. While it may take several months before it can take full effect, its effectiveness can last up to six months or more.

- Physical Therapy and Exercise – Exercise helps strengthen the supporting muscles of your knees. Physical therapists can also help design an individualized treatment plan to help manage your pain and strengthen the knee muscles.
- Weight Loss – Did you know that gaining a single pound places three extra pounds of pressure on your knee?
- Nutritional Supplements – Glucosamine and chondroitin help patients with osteoarthritis. SAMe is another popular supplement that provides relief from knee pain to keep you moving comfortably.
- Arthroscopic Surgery – Arthroscopic surgery involves the insertion of a thin tube with a tiny camera into a small incision of your skin to enable the surgeon to view and remove loose bones or cartilage pieces that caused the pain. The recovery is not usually painful and takes a short period for arthroscopic patients to resume back to their normal activities.
If the above remedies fail, it may be time to consider knee replacement surgery.
Partial versus Total Knee Replacement
Knee replacement is a common procedure for people suffering from osteoarthritis and other pain knee conditions. This surgical procedure involves the removal of all or part of the knee joint and replacement of damaged parts with an artificial plastic or metal joint. While recovery could take several months, knee replacement provides long-term or even lifetime relief from pain.
A partial knee replacement surgery only involves the replacement of the affected knee compartment, preserving the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. Factors that make you an ideal candidate for partial knee replacement include:
- Minimal knee deformity
- Weighing less than 180 lbs.
- Sedentary lifestyle
- A good range of motion prior to the surgery
While partial knee replacement may seem like a less complex option, it is crucial to be aware of the differences between a partial and a total knee replacement surgery. As a candidate for knee replacement surgery, you should understand that each surgical procedure is unique and has its own set of benefits and risks after the surgery.
| Benefits |
Risks |
| Retains most of the knee tissues |
Higher risk of revision surgery |
| Less bone and soft tissue dissected |
Knee function could potentially worsen after revision of partial knee replacement |
| Risk of complications (blood loss, transfusions, and blood clots) is low |
Revision is often a complex procedure |
| Quicker recovery time |
The lifespan of partial knee replacement components is lower than that of the components used in total knee replacement |
| Better range of overall mobility and greater patient satisfaction with the outcome |
|
As its name implies, total knee replacement surgery involves the removal of the entire joint and replacing it with an artificial knee component. It is a safe and effective solution for treating the pain and stiffness caused by knee osteoarthritis.
Patients suffering from persistently painful, severe bone-on-bone arthritis of the knee that cannot be controlled with conservative treatment options may be ideal candidates for a total knee replacement surgery. Other factors include:
- Knees that feel unstable and about to ‘give out’
- Knee or leg deformity
- Pain and stiffness in your knee due to inflammatory knee arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Chronic knee pain that prevents you from doing simple activities
Total knee replacement surgery does not have age or weight restrictions. Your healthcare professional will evaluate your pain and degree of disability when forming a recommendation for surgery.
| Benefits |
Risks |
| Total knee replacement components can last about 10 to 15 years |
Greater cost |
| Greater patient satisfaction |
Wear and tear of the implant due to heavy use |
| Higher functional scores |
Scar tissues |
| Less pain and greater knee mobility after surgery |
Neurovascular damage |
|
Infection in the artificial joint |
While partial and total knee replacement surgeries have higher success rates, some patients may experience a bit of pain and stiffness after the operation. The surgeon may have fixed the problem, but it is your turn to make sure that the surgery is a complete success. It means restoring the strength and mobility of your knee.
Since 1995, Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Centres of Ontario has been serving clients in six locations: Oshawa, Scarborough, Ajax, Whitby, Mississauga, and Scarborough West. Our team of professional healthcare professionals welcomes knee replacement patients and provides a personalized treatment plan to help them get back on their feet and resume their normal daily activities. Call us at (905) 579-9938 to book a physiotherapy service in Oshawa.